Development
-
lacking sufficient money to live at a standard considered comfortable or normal in a society.
-
having a great deal of money or assets
-
A state of being poor.
-
The act or process of improving or becoming better.
-
Th basic monetary unit for many countries including the USA.
-
money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments.
-
Usually a numerical measure of quality of life in a country. Indicators are used to illustrate progress of a country in meeting a range of economic, social, and environmental goals.
-
the total value of goods produced and services provided by a country during one year, equal to the gross domestic product plus the net income from foreign investments.
-
Gross Domestic Product - the total value of goods produced and services provided in a country during one year.
-
Gross National Income - the sum of a country's gross domestic product (GDP) plus net income (positive or negative) from abroad.
-
Purchasing power parity is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare how much you can buy with different currencies in different countries.
-
for each person; in relation to people taken individually.
-
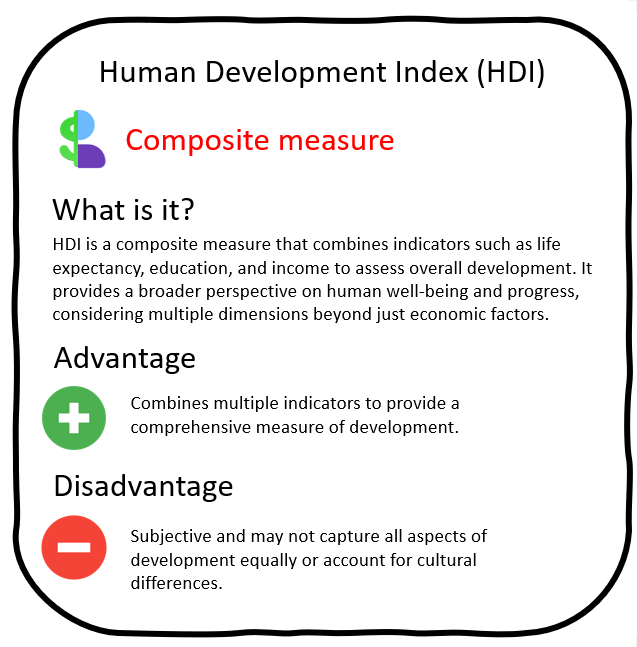
The Human Development Index is a composite index of life expectancy, education, and per capita income, which are used to rank countries.
-
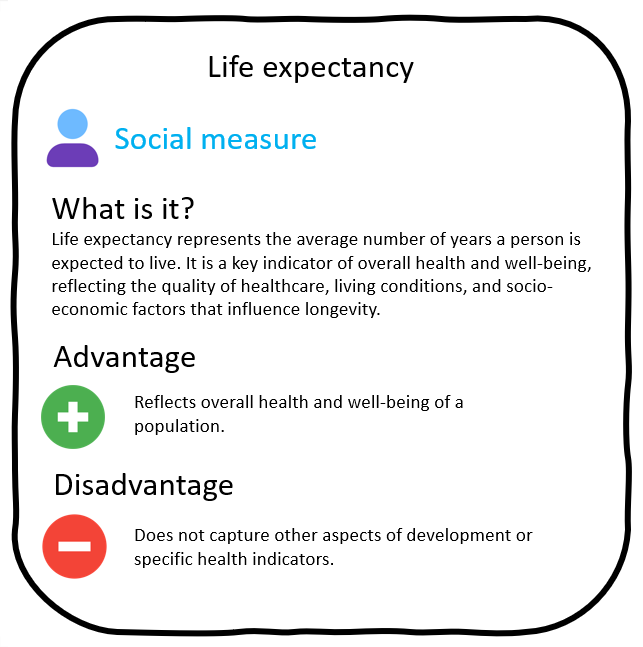
the average period that a person may expect to live
-
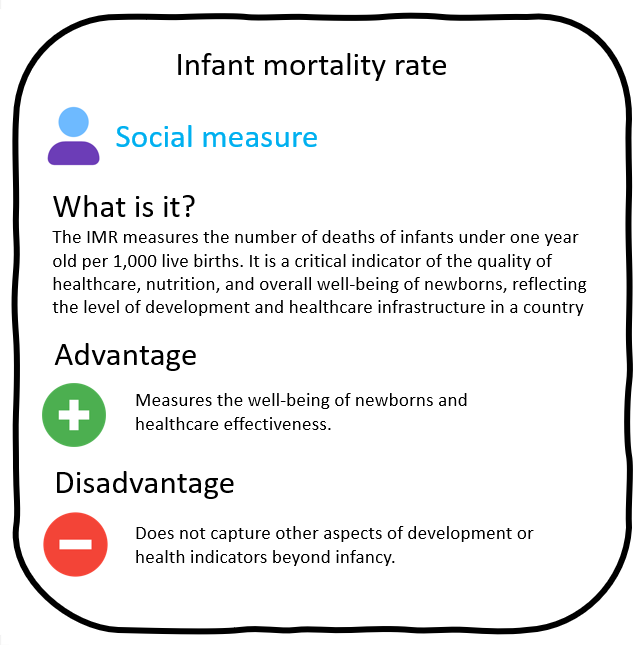
the number of infant deaths for every 1,000 live births.
-
the percentage of the population of a given age group that can read and write.
-
the number of years during which a 2-year-old child can expect to spend in schooling.
-
The number of calories an individual consumes in one day.
-
the World Bank is an international organization dedicated to providing financing, advice, and research to developing nations to aid their economic power.
-
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an organization of 190 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability
-
Low income country
-
High Income Country
-
Newly industrialized country.
-
dishonest or fraudulent conduct by those in power, typically involving bribery.
-
A struggle between two or more countries normally involving the military.
-
almost or entirely surrounded by land; having no coastline or seaport
-
the relation between two expressions that are not equal, for example two groups within the same society earning dramatically different wages.
-
a government, levies or imposes a financial obligation on its citizens or residents
-
the action of buying and selling goods and services.
-
bring (goods or services) into a country from abroad for sale
-
send (goods or services) to another country for sale.
-
the dependence of two or more people or things on each other.
-
the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period.
-
the amount by which the value of a country's exports exceeds the cost of its imports.
-
the amount by which the cost of a country's imports exceeds the value of its exports.
-
trade between companies in developed countries and producers in developing countries in which fair prices are paid to the producers.
Start of Content
What is development?
Development refers to the progress and improvement of a country or region in various aspects, including social, economic, and environmental factors. It involves positive changes that lead to a better quality of life for the people living in that area. Development can be measured by looking at indicators such as economic growth, infrastructure development, access to education and healthcare, and overall well-being of the population.
What is wealth?
Wealth refers to the abundance of valuable resources, assets, or possessions that an individual, community, or country possesses. It can include financial resources, natural resources, infrastructure, and human capital. Wealth is often associated with economic prosperity and can contribute to the development of a country. However, it is important to note that wealth alone does not guarantee a high quality of life or well-being for all individuals within a society.
What is quality of life?
Quality of life refers to the overall well-being and satisfaction that individuals experience in their daily lives. It encompasses various aspects such as access to basic needs, healthcare, education, employment opportunities, social relationships, and personal safety. A high quality of life indicates that individuals have a good standard of living and enjoy a range of opportunities and amenities that contribute to their happiness and fulfillment.
What is standard of living?
Standard of living refers to the level of material comfort and well-being enjoyed by individuals or households within a particular society. It is often measured by factors such as income, housing conditions, access to basic services, and availability of consumer goods. A high standard of living implies that individuals have access to a decent income, adequate housing, healthcare, education, and other necessities that contribute to their overall well-being.
How can we measure the development of countries?
The development of countries can be measured using various indicators and indices. Some commonly used measures include Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country, Human Development Index (HDI), which considers factors like life expectancy, education, and income. These measures provide insights into the economic, social, and human development of a country and help in comparing them.
What is the development gap?
The development gap refers to the disparity in levels of development between different countries or regions. It highlights the differences in economic growth, infrastructure, access to resources, education, healthcare, and overall well-being. The development gap can be observed both within and between countries, with some regions experiencing higher levels of development while others lag behind. Addressing the development gap is crucial for achieving global equity and ensuring that all individuals have equal opportunities and access to resources.
Development indicators


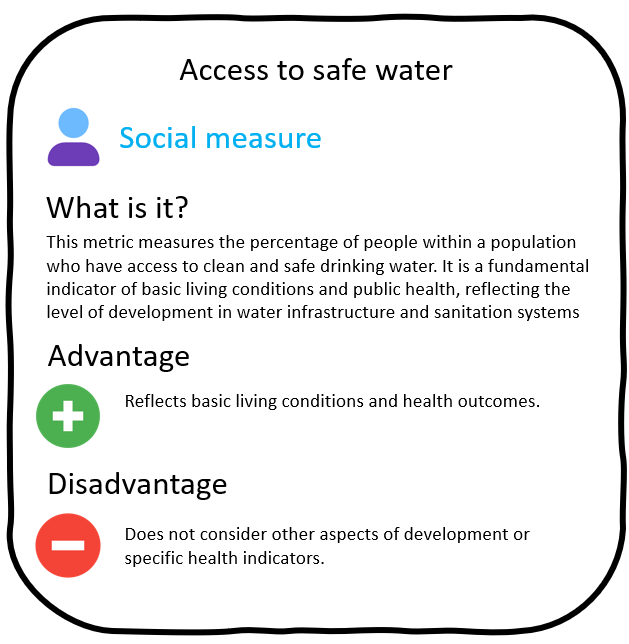
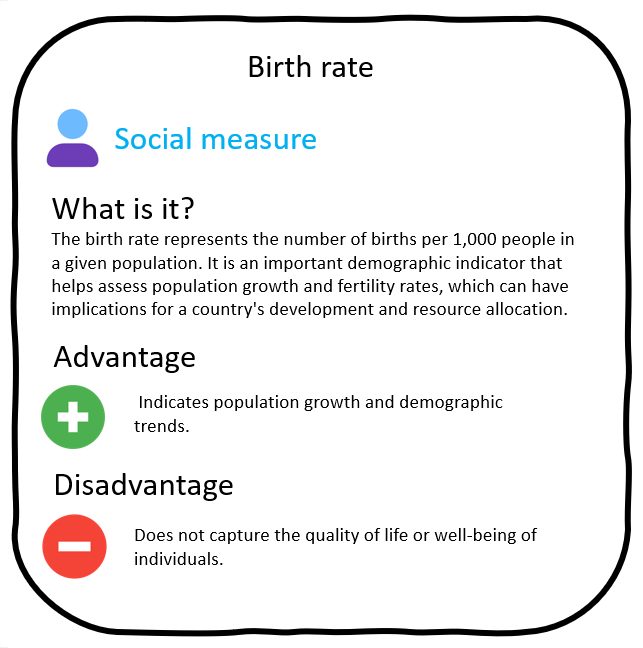


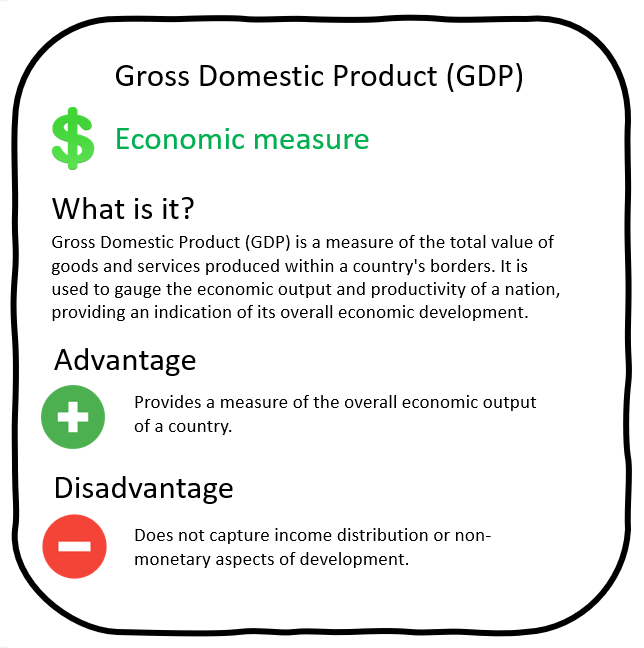
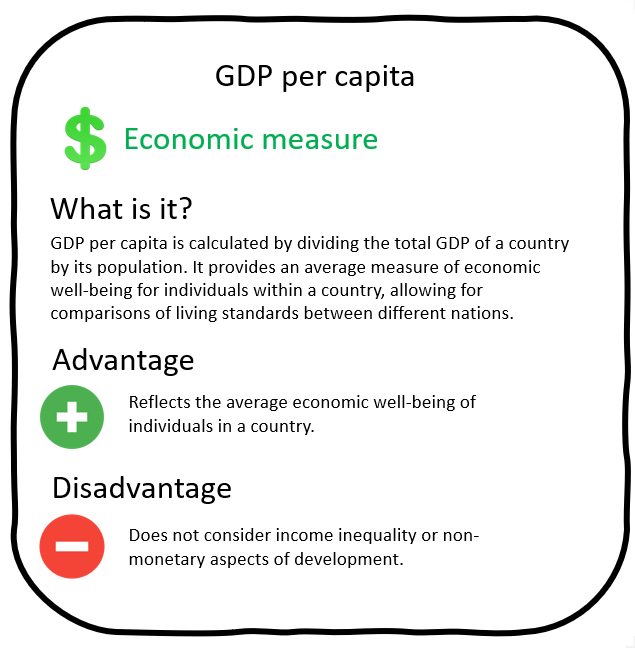
Which countries are developed?
The Brandt Line
The Brandt Line is a concept that divides the world into two parts based on their level of development. It was proposed by Willy Brandt, a former German Chancellor, in the 1980s. The line separates the more developed countries in the northern hemisphere from the less developed countries in the southern hemisphere. A positive aspect of the Brandt Line is that it highlights the economic disparities between countries in the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere. However, critics argue that the Brandt Line oversimplifies the complexities of development and fails to consider other factors such as political stability, cultural differences, and historical contexts that contribute to a country's development. Additionally, it can perpetuate stereotypes and reinforce a sense of superiority among developed nations. It is important to approach the Brandt Line with a critical mindset and consider multiple perspectives when analyzing global development.
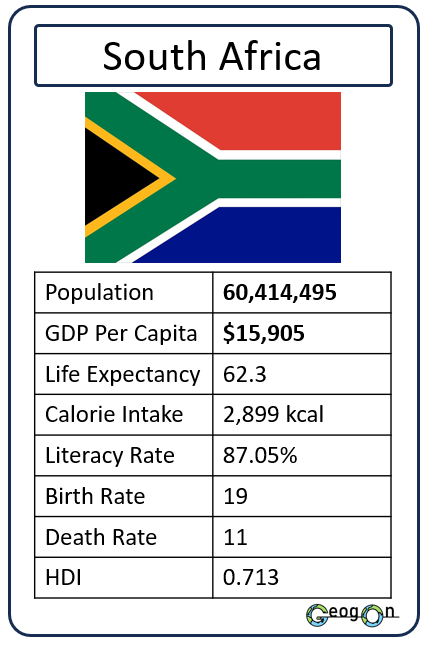
Example Countries
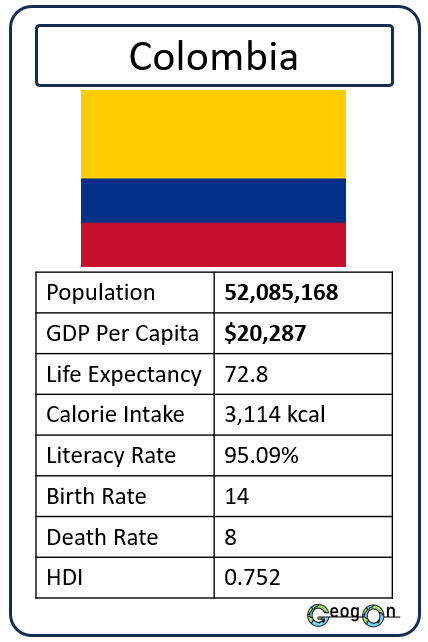
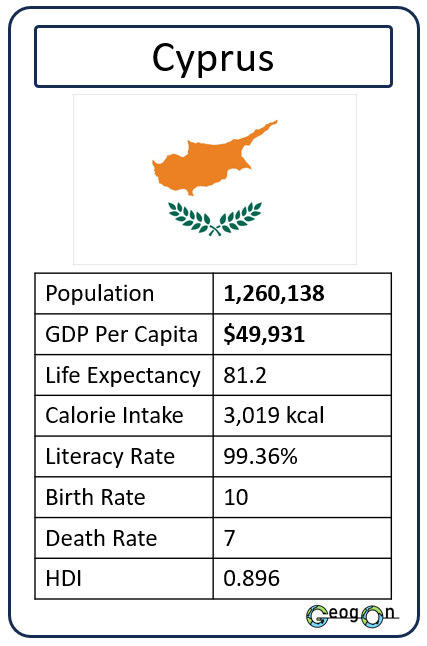
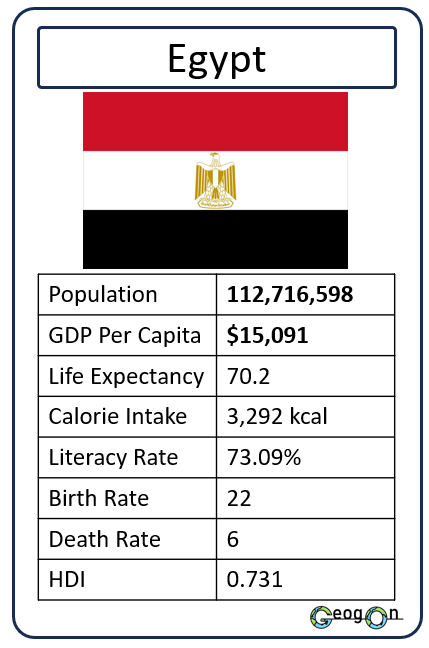
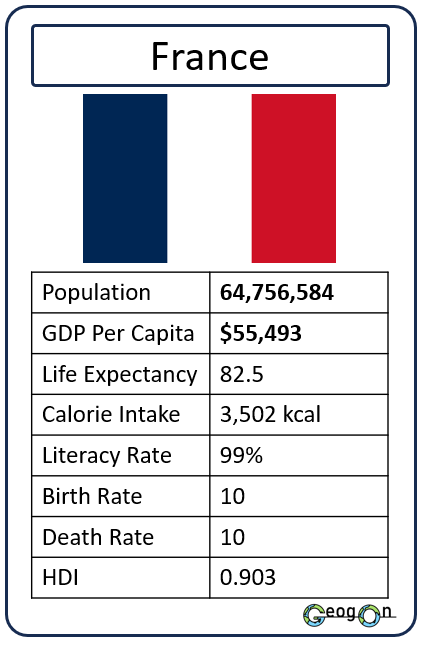
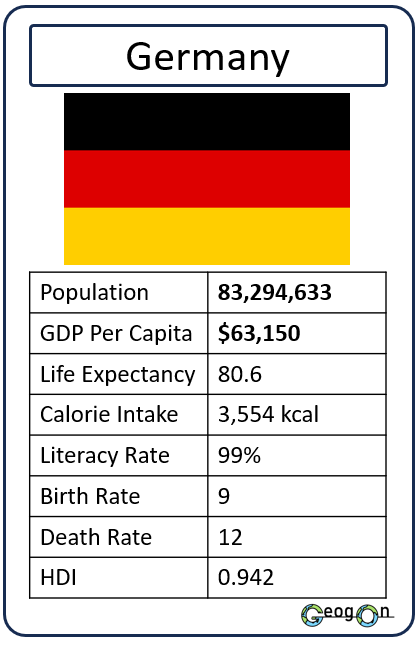
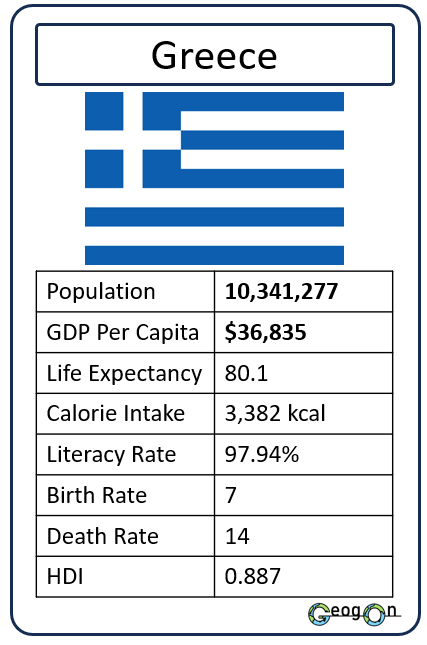
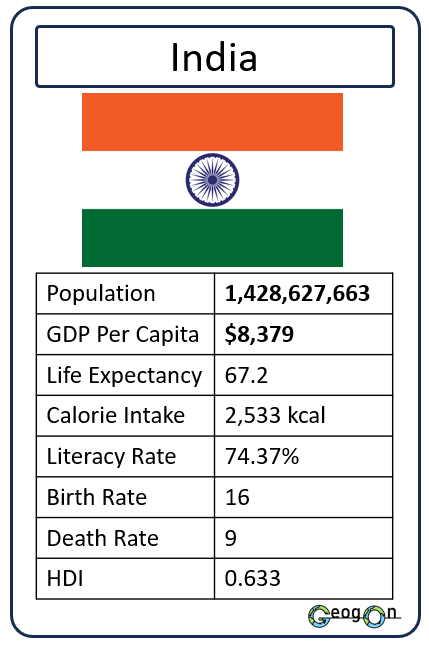
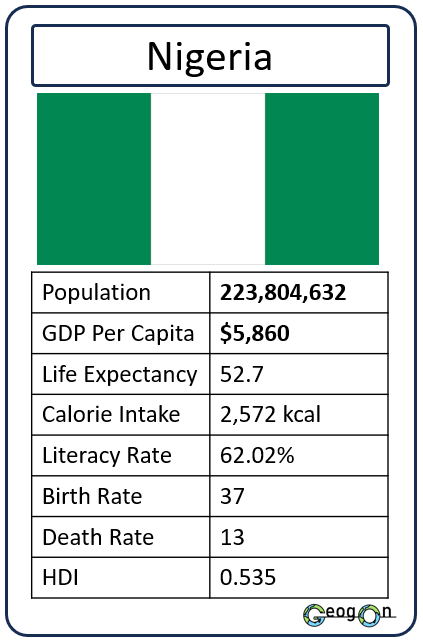
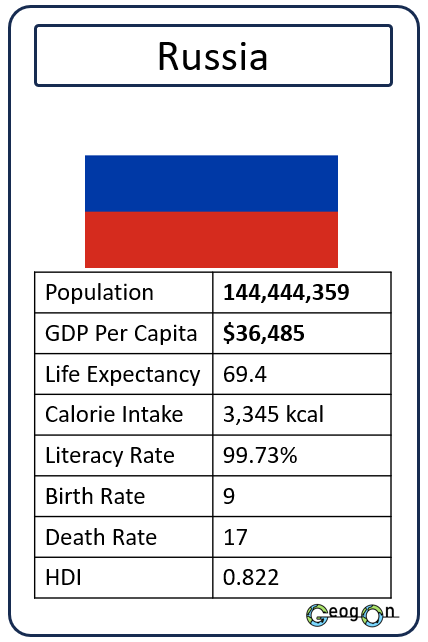
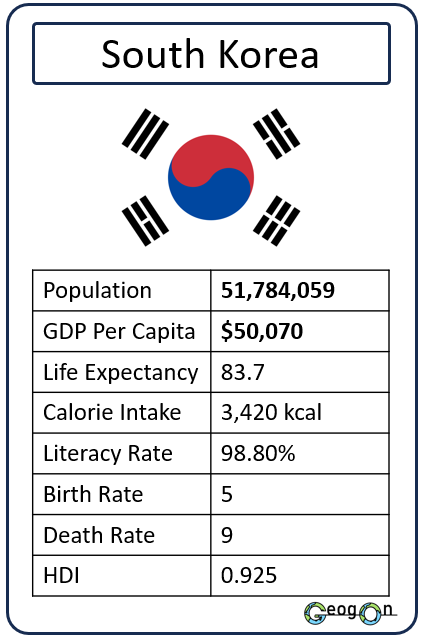
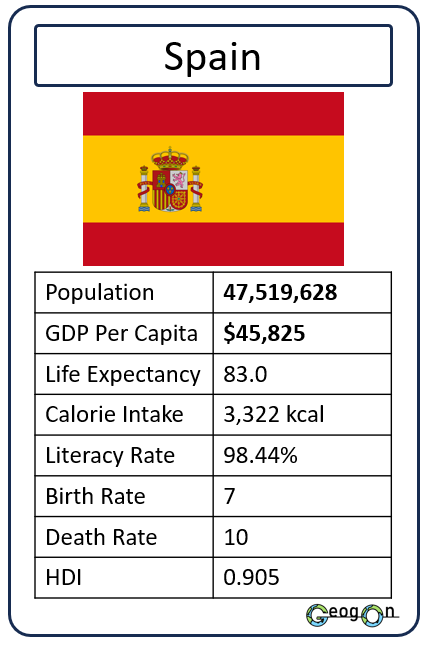
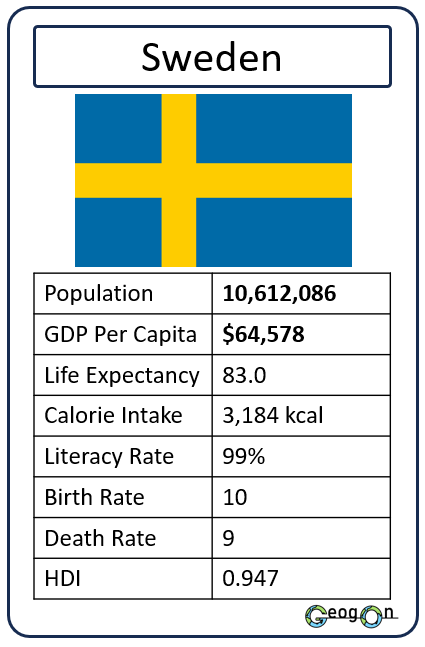
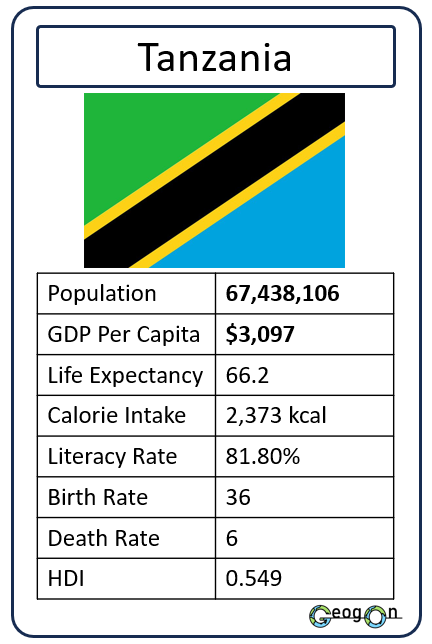
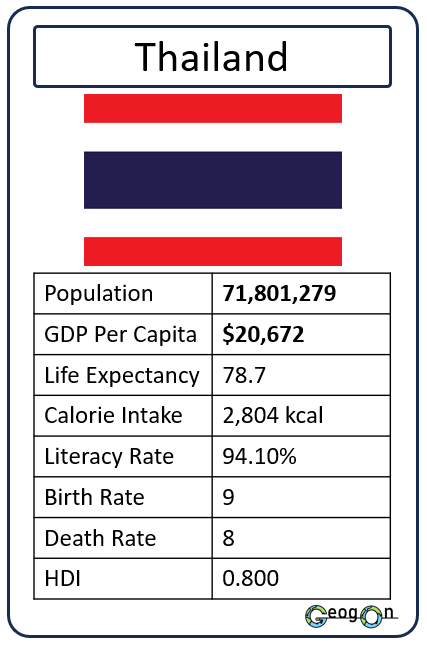
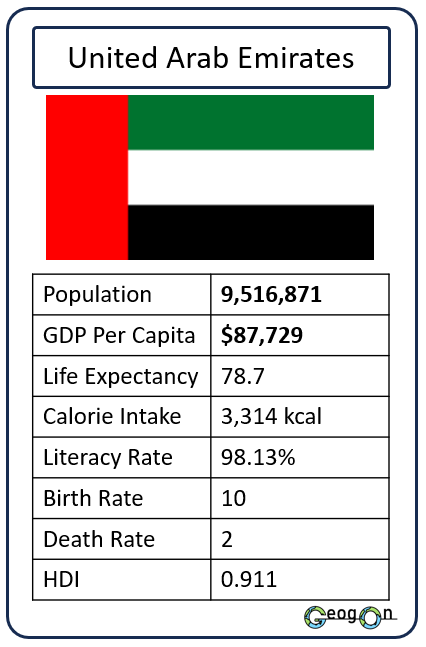
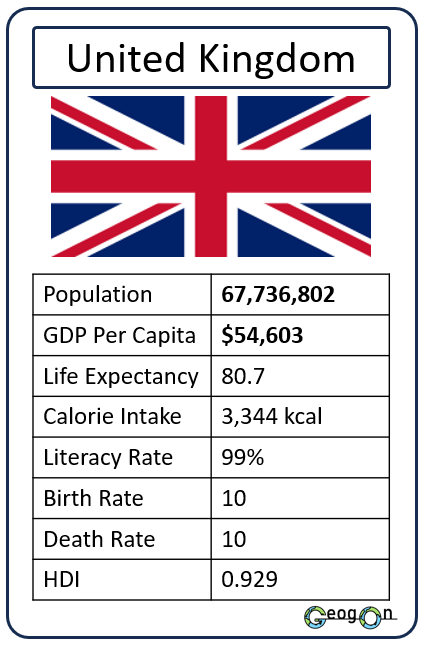
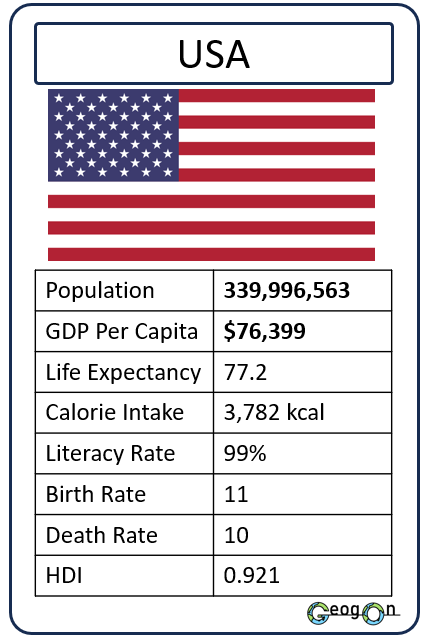
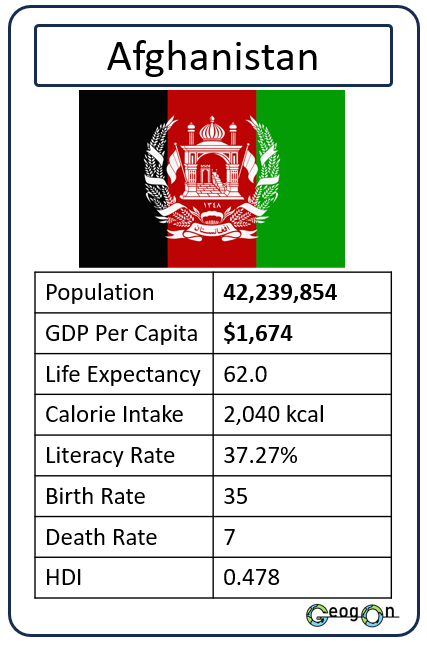
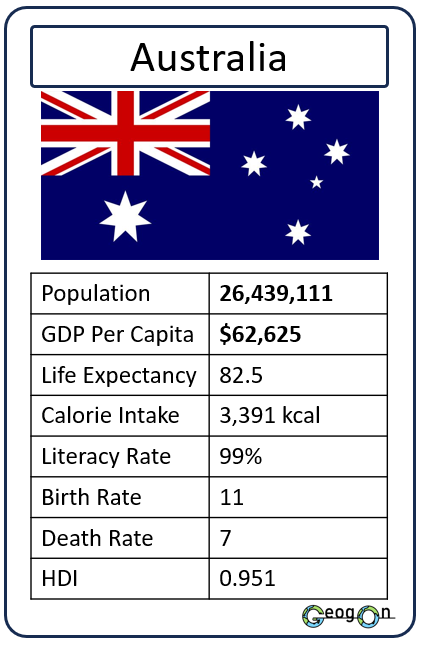
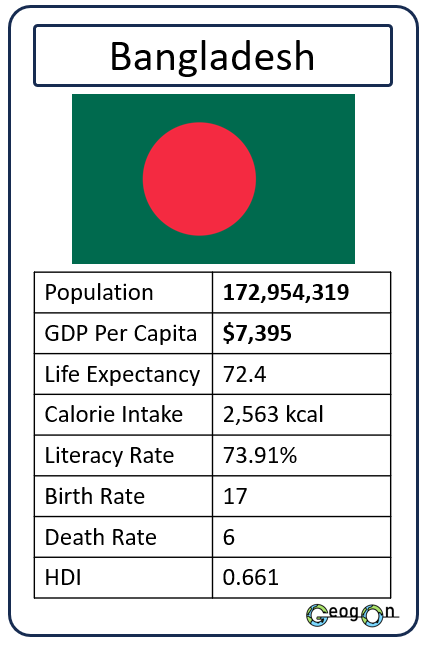
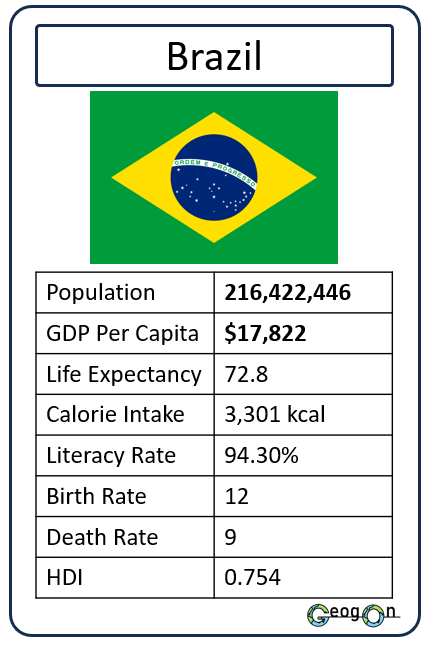
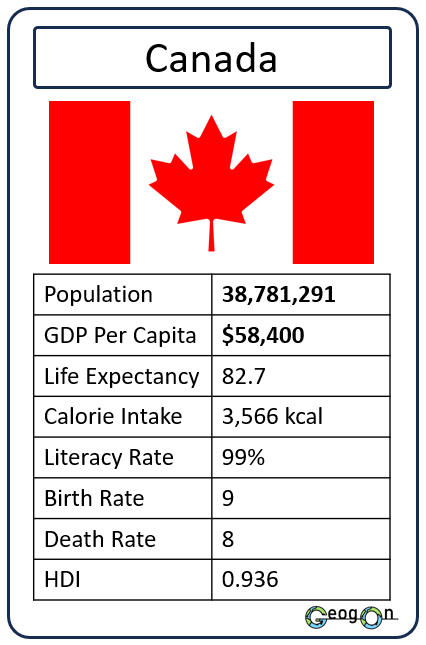
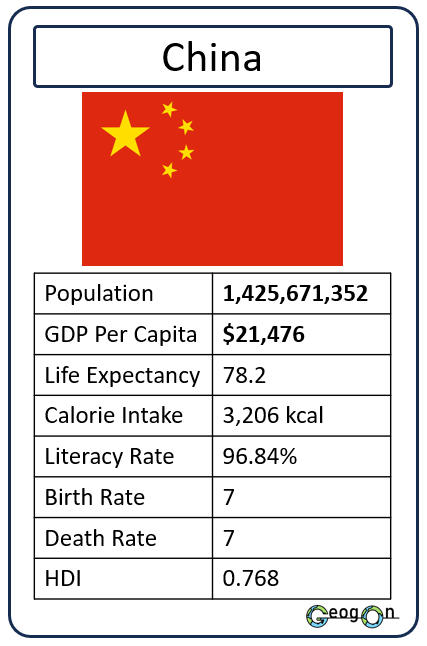
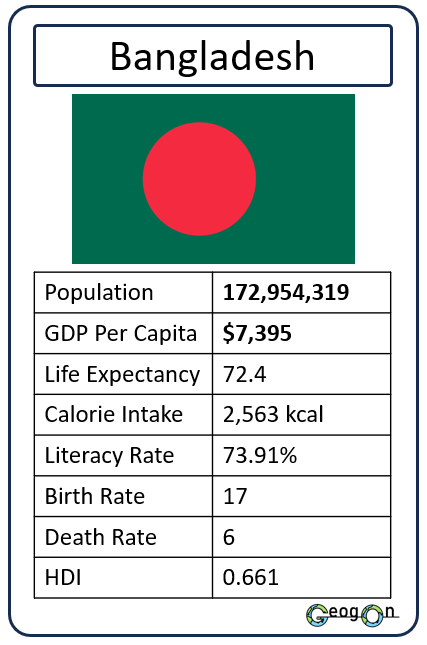
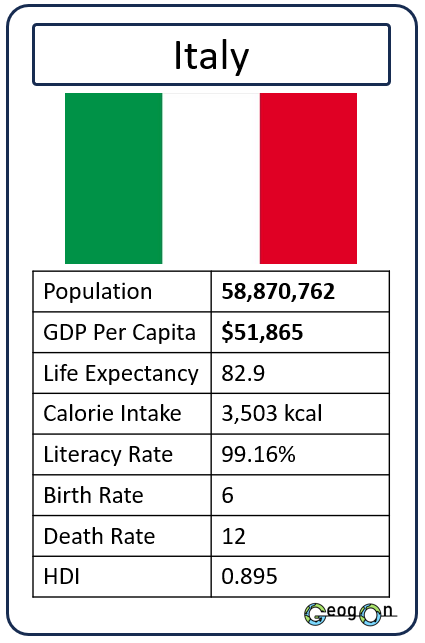
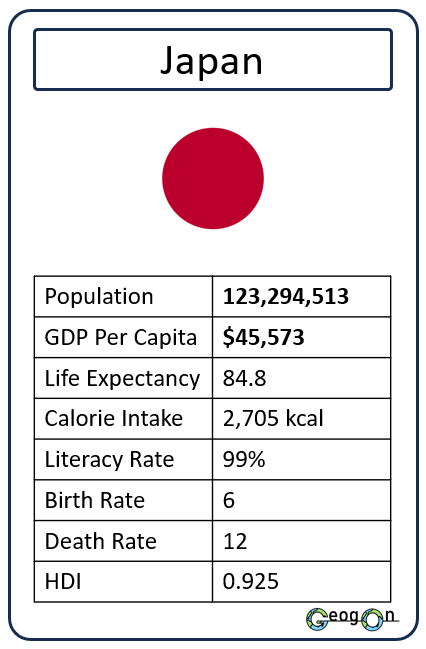
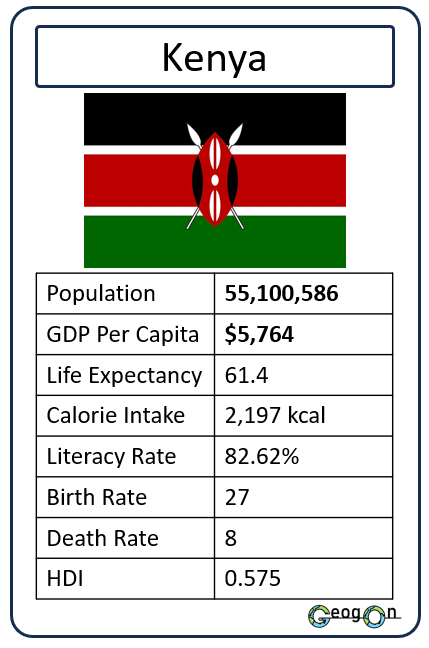
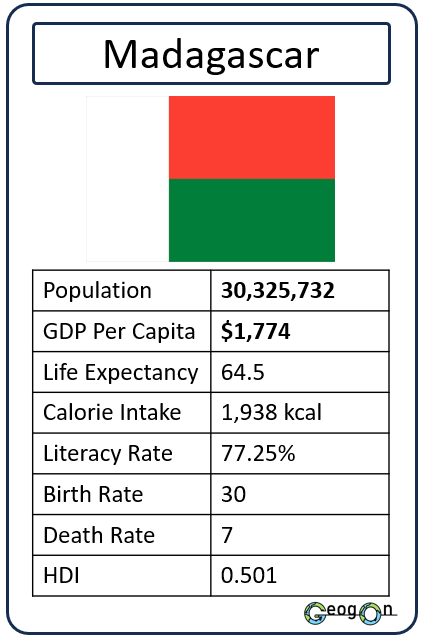
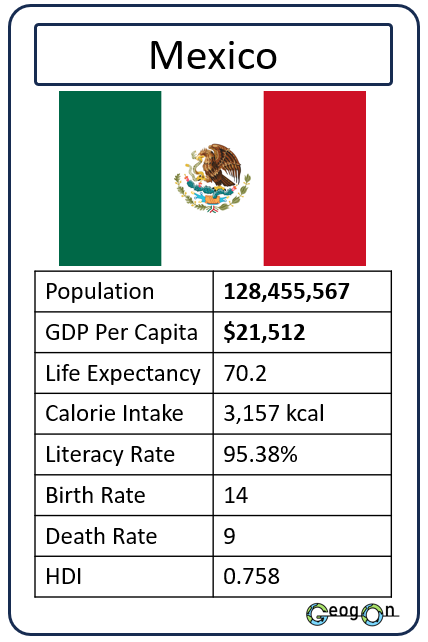
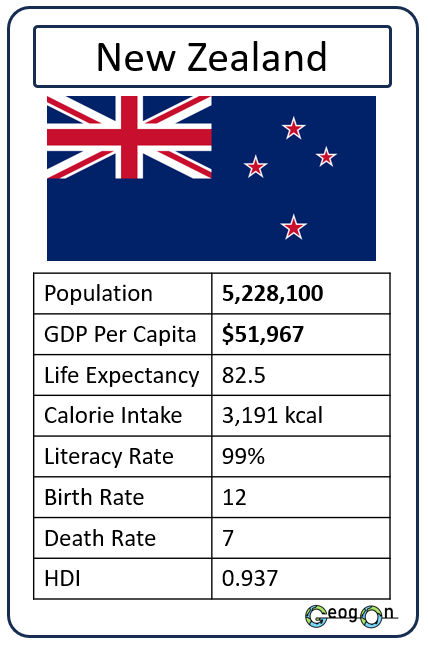
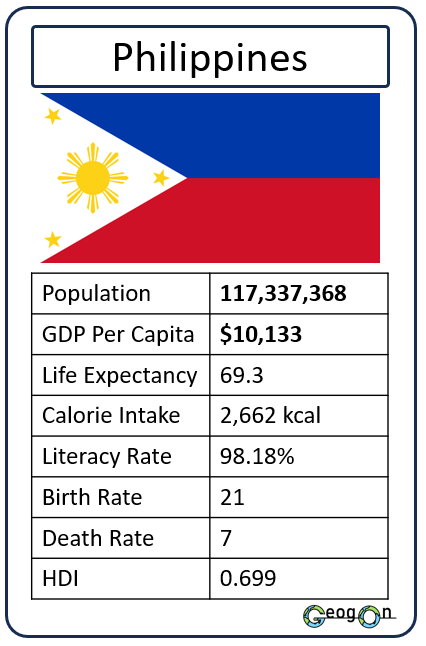
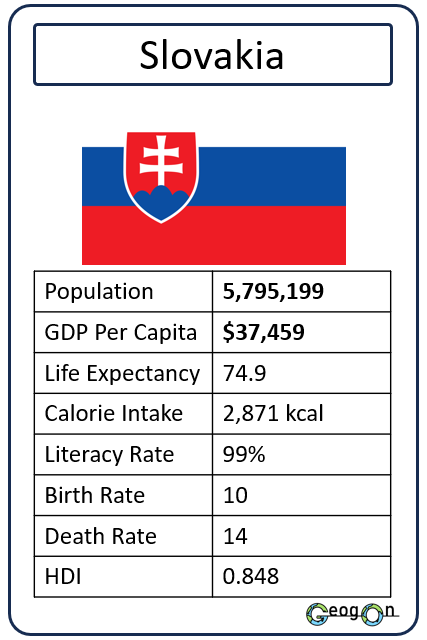
How did the development gap grow?
Comparing a typical day in Malawi and Singapore
Malawi
1 Malawian Kwacha equals 0.0009 United States Dollar
Singapore
1 Singapore Dollar equals 0.74 United States Dollar
Chocolate Trade in Ivory Coast (Côte d'Ivoire)
Ivory Coast is one of the largest producers of cocoa beans in the world, which are the main ingredient in chocolate. The cocoa industry is vital to the country’s economy, but it also faces several serious challenges.
Farmers’ Wages
Cocoa farmers in Ivory Coast typically earn very low wages. Many small-scale farmers receive around $1 to $2 per day, which is far below the minimum wage in many countries. Despite Ivory Coast being a leading exporter of cocoa, farmers struggle to make ends meet because the prices they receive for cocoa beans are often controlled by international companies. Farmers often live in poverty, with little access to education, healthcare, or basic infrastructure.
Child Labour
Child labour remains a major issue in the cocoa industry. Despite efforts from the government and international organizations, many children are still involved in hazardous work on cocoa farms. Children often work in dangerous conditions, carrying heavy loads, using sharp tools, and applying harmful chemicals. Many children do not attend school, and some work to support their families due to economic hardship.
Estimates suggest that over 2 million children work in cocoa farms across West Africa, including Ivory Coast. These children often face abuse and exploitation, and their education is severely disrupted, trapping them in a cycle of poverty.
Fairtrade
FairTrade is a global movement that aims to ensure that farmers and workers in developing countries receive fair wages and work under safe, ethical conditions. The FairTrade certification system guarantees that products, such as chocolate, coffee, and clothing, are produced and traded in a way that promotes social, environmental, and economic fairness.
How does it work?
Does it work?
Others Ways to Help: Aid
What is Aid?
Aid refers to the assistance provided by one country, organization, or individual to help another, typically to support economic development, improve living conditions, and address humanitarian needs. It can come in many forms, such as financial support, food and medical supplies, technology, education, and skills training. Aid is often directed to countries facing poverty, conflict, natural disasters, or economic hardship.
Corruption in Aid
Aid often faces issues with corruption, where funds are misused or diverted before reaching those in need. Picture A shows officials taking a portion of aid, highlighting how corruption prevents the intended recipients from receiving full support.
Dilution of Aid
Aid can be diluted as it moves through different layers of administration. Picture B shows aid being reduced at each step, emphasizing how inefficiency and red tape mean less help reaches the people who need it most.





















