The Middle East
-
A region refers to a specific area on Earth that shares common characteristics, such as physical features, climate, or cultural aspects.
-
Transcontinental means something that spans across or connects multiple continents.
-
Human characteristics refer to the features or attributes that are created or influenced by human beings, such as buildings, cities, language, customs, and traditions.
-
Physical characteristics are the natural features of an area, including landforms (mountains, rivers, etc.), climate, vegetation, and wildlife.
-
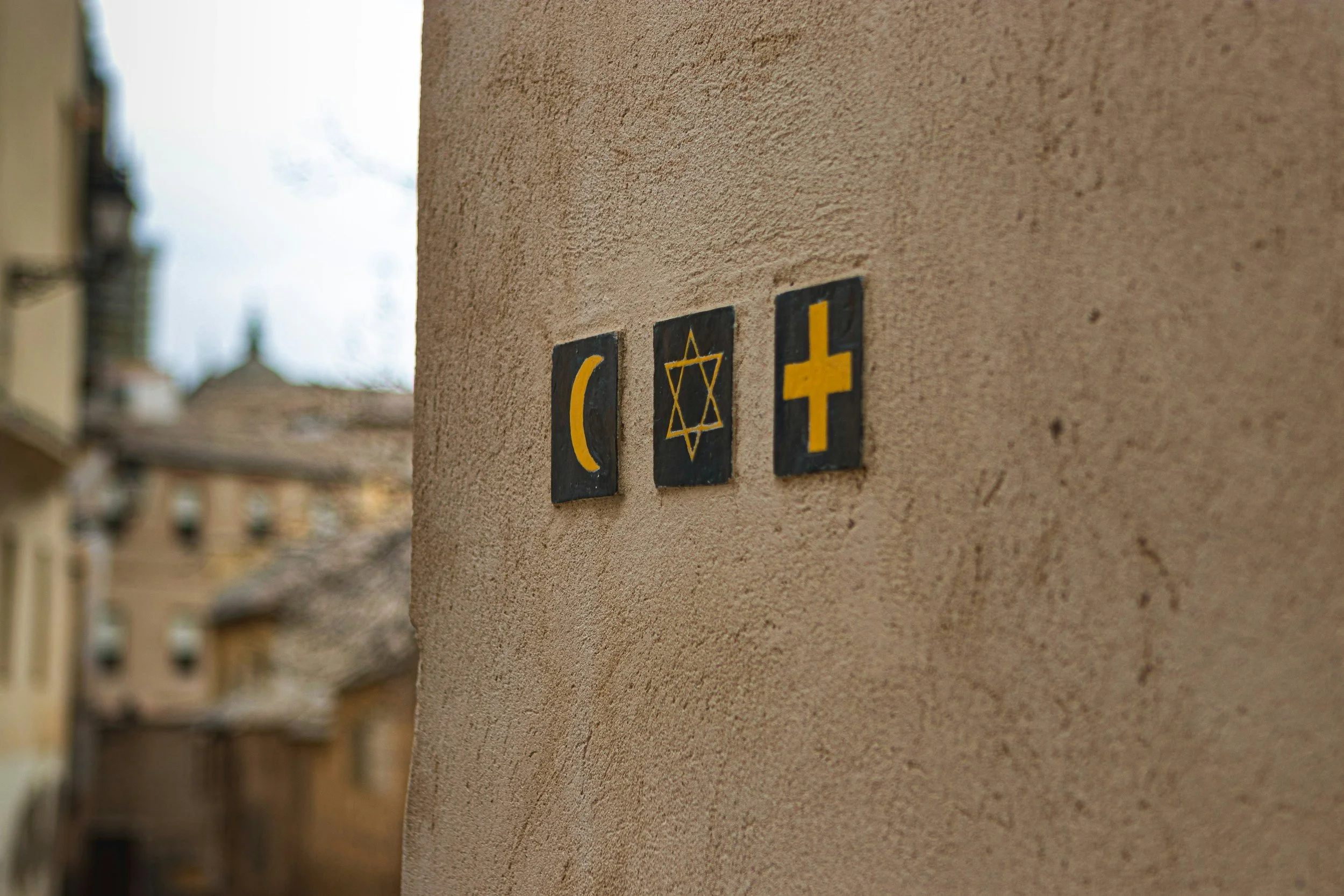
Christianity is a major world religion based on the teachings of Jesus Christ, emphasizing love, forgiveness, and salvation through faith in Jesus.
-
Islam is a major world religion founded by Prophet Muhammad, with its followers known as Muslims. It is based on the belief in one God (Allah) and the teachings of the Quran.
-
Judaism is one of the oldest monotheistic religions, with its followers known as Jews. It is based on the belief in one God and the teachings of the Torah.
-
A desert is a barren area with little or no vegetation, typically characterized by extreme heat, aridity, and minimal rainfall.
-
A gulf is a large area of the ocean or sea that is partially enclosed by land, with a narrow opening.
-
Climate refers to the long-term weather patterns and conditions of a particular region, including temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and seasons.
-
A climate graph is a visual representation of a region's climate data, showing the average temperature and precipitation throughout the year.
-
Arid describes a climate or environment that is extremely dry, with little rainfall and limited vegetation.
-
A biome is a large ecological region characterized by distinct plant and animal communities adapted to specific climate conditions.
-
Vegetation refers to the plant life in a particular area or region.
-
Adaptation refers to the process by which organisms adjust to their environment in order to survive.
-
Nocturnal describes animals or activities that are primarily active during the night.
-
Crude oil is a naturally occurring, unrefined petroleum product that is extracted from the Earth and used as a source of energy.
-
Oil refers to various types of liquid hydrocarbons, including crude oil, that are used as sources of energy and for various industrial purposes.
-
Oil reserve refers to the estimated amount of oil that can be economically extracted from a particular oil field or region.
-
Development refers to the process of economic, social, and technological progress that improves the well-being and quality of life for individuals and societies.
-
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a measure that assesses a country's level of development based on factors such as life expectancy, education, and income.
-
Life expectancy is the average number of years a person is expected to live, based on factors such as health, healthcare access, and living conditions.
-
Education refers to the process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes through formal or informal means.
-
Income refers to the money or financial resources that an individual or household earns from various sources, such as employment or investments.
-
Trade refers to the exchange of goods and services between individuals, businesses, or countries.
-
Import refers to the act of bringing goods or services into a country from another country for sale or use.
-
Export refers to the act of sending goods or services from one country to another for sale or use.
-
A dam is a barrier or structure built across a river or watercourse to control or regulate the flow of water, often used for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, or water supply.
-
Hydroelectric refers to the generation of electricity using the power of flowing or falling water.
-
Meeting the needs of today without damaging the resources and chances of tomorrow.
-
Socially sustainable refers to practices or actions that promote social well-being, equality, and justice within a community or society.
-
Economically sustainable refers to practices or actions that support long-term economic growth, stability, and prosperity without depleting resources or causing harm to the economy.
-
Environmentally sustainable refers to practices or actions that protect and preserve the natural environment, biodiversity, and ecosystems for future generations.
-
Culture refers to the shared beliefs, values, customs, traditions, arts, and social institutions of a particular group or society.
-
Human rights are the basic rights and freedoms to which all individuals are entitled, regardless of their nationality, race, gender, or other characteristics. They include rights such as the right to life, liberty, equality, and freedom of expression.
Start of Content
Location of the Middle East
The Middle East is a large area located to the west of Asia. It is also to the southeast of Europe and to the north of Africa. The Middle East is surrounded by several important bodies of water. To the north, it is bordered by the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. To the west, you find the Mediterranean Sea, and to the south, the Red Sea and the Arabian Sea. This region is positioned along the Tropic of Cancer, making it a central area connecting three continents.
Defining the Middle East: The Challenge
The term "Middle East" includes many countries, cultures, and landscapes, but not everyone agrees on which countries are part of the Middle East. People view and understand this region differently, based on their backgrounds and knowledge. The Middle East is a large area that stretches across parts of three continents: Asia, Africa, and a small portion of southeastern Europe, which adds complexity to its definition. For instance, while many people worldwide might consider Egypt part of the Middle East, some Egyptians may not see themselves as part of this region. This example shows that how we define a region can vary and depends on various factors such as history and cultural perspectives.
What is the Middle East?
The Middle East is a large area that includes parts of three continents: Asia, Africa, and Europe. It is known for its diverse cultures and is the birthplace of three major world religions: Christianity, Islam, and Judaism. The biggest country in the Middle East is Saudi Arabia, and the smallest is Bahrain. The name "Middle East" was first used by the British in the 1850s.
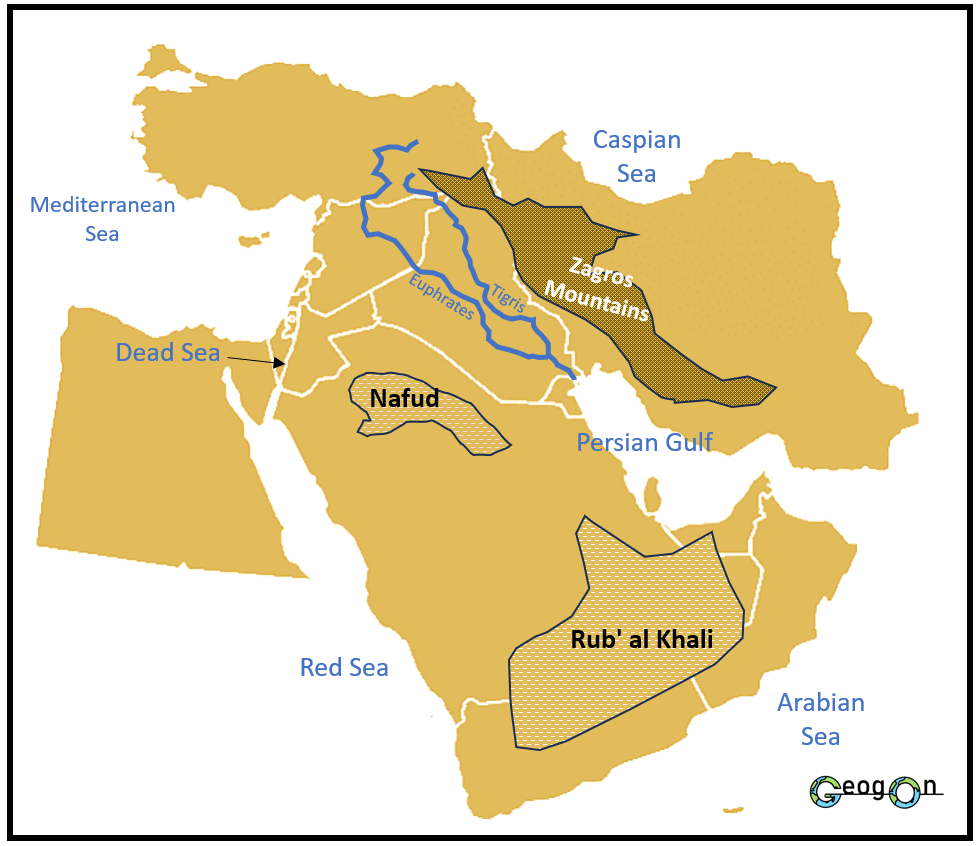
Physical Features of the Middle East
These varied landscapes not only define the region's physical appearance but also influence the lifestyles and economies of the people living there. For instance, the availability of oil in the Persian Gulf has led to economic prosperity for countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, while the fertile lands of the Tigris-Euphrates river system have supported agriculture for thousands of years.
Persian Gulf: This body of water lies between the Arabian Peninsula and Iran. It is a crucial area for the world's oil production and has rich fishing grounds and extensive coral reefs.
Nafud Desert: Located in northern Saudi Arabia, this desert consists of about 2,500 square miles of sand dunes. It receives enough winter rain to support grazing in the winter and spring months.
Tigris River: Flowing through Turkey and Iraq, this river is essential for irrigation and is home to over 50 species of fish. It has many dams to control flooding.
Euphrates River: Along with the Tigris, the Euphrates supports the fertile region known as Mesopotamia, historically known as the "cradle of civilization." It flows through Turkey, Syria, and Iraq.
Zagros Mountains: These mountains stretch across Iran, providing a natural barrier and influencing the climate of the region. They are also important for their biodiversity.
Rub' al Khali (Empty Quarter): One of the largest sand deserts in the world, covering much of the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula. It is noted for its extreme heat and aridity.
Dead Sea: Bordering Jordan to the east and Israel and Palestine to the west, this salt lake is the lowest point on Earth's surface on dry land and is famous for its high salinity which makes swimming similar to floating.
What Are Deserts?
Deserts are very dry places where it hardly rains; they get less than 250 millimeters (about 10 inches) of rain each year. These areas have very little plant life because there is not enough water for most plants to grow.
Deserts are often thought of as very hot, but they can be cold too. The amount of rain is what really makes a place a desert, not just the temperature.
Hot and Cold in One Day: The Sahara Desert gets extremely hot during the day, sometimes over 50°C (122°F). At night, it can get cool, even down to 0°C (32°F), because there are no clouds to keep the heat in.
Cold Winters: The Gobi Desert in Asia has very cold winters. It is high up and far from the sea, so it can even snow there.
Antarctica: A Frozen Desert: Antarctica is the biggest desert in the world and the coldest place on Earth. It is very dry and windy, with temperatures that can drop to -60°C (-76°F) in winter. It gets very little rain, just like other deserts.
The Climate
What is a Climate Graph?
Climate graphs are visual tools used to show the climate data of a specific location over a period, usually a year. A climate graph combines a line graph and a bar graph on the same chart.
Temperature: This is usually shown with a line graph. The line goes up and down to represent how the temperature changes each month.
Precipitation: This is shown with a bar graph. Each bar represents the amount of rain (or snow) that falls in a month.
Saudi Arabia has a desert climate, which means it is generally hot and dry:
Temperature: The line on the graph rises in the hot months from April to September, where temperatures can reach high levels, often above 30°C. In the cooler months, from November to March, the line drops to show lower temperatures, although it still remains quite warm, around 15°C to 20°C.
Precipitation: The bars for rainfall are low, reflecting the dry conditions. Most colder months, November to April show very little precipitation, indicating 12 mm of rain or less. June to September receives no rainfall.
Living in Deserts
How Animals Adapt to the Desert
Desert animals have developed unique adaptations to survive in extreme heat and aridity. For example:
Camels have thick eyelashes, ear hair, and nostrils they can close to keep out sand during storms. They also have a unique ability to fluctuate their body temperature to conserve water.
Fennec Foxes, with their large ears, enhance their ability to lose heat and stay cool. They are also nocturnal, which helps them avoid the daytime heat.
Sand Vipers burrow into the sand to stay cool during the day and come out at night to hunt. Their coloration blends into the sandy environment, providing camouflage from predators and prey.
Addax Antelopes can go nearly their entire lives without drinking water, deriving moisture from the food they eat and conserving water through minimal sweating.
How People Live in the Desert
People living in desert regions have developed various cultural and technological adaptations to thrive under harsh conditions:
Bedouin tribes wear light-colored, loose-fitting clothes that cover their whole bodies to protect against the sun while allowing air circulation that helps keep them cool.
Houses in many desert communities are often built with thick mud walls that insulate against heat during the day and retain warmth at night. The flat roofs are used to sleep on during hot nights, and small windows prevent excessive heat gain.
Diet adaptations include eating moisture-rich foods.
Lifestyle leading a nomadic lifestyle, which involves moving from place to place to follow available resources.
Water conservation techniques such as dew harvesting and the use of ancient aqueducts or modern drip irrigation systems to maximize the efficiency of water use in agriculture.
How Plants Survive in the Desert
Desert plants have evolved several fascinating strategies to cope with water scarcity and intense heat:
Cacti store large amounts of water in their fleshy stems and have spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss. Their extensive root systems spread wide to collect as much moisture as possible.
Creosote bushes exude a resin that covers their leaves, significantly reducing water loss and reflecting sunlight, which keeps them cooler.
Date Palms use their deep root systems to tap into underground water sources, and their leaves are structured to minimize water loss.
Acacia trees have small, thick leaves with few stomata to minimize water evaporation. They often host ants that protect the tree from herbivorous insects.
What is Development?
Development is about improving the quality of life for people in a community or country. It involves more than just increasing wealth; it includes making sure people have access to essential services and opportunities. Important aspects of development are clean water, reliable healthcare, good education, efficient transportation, gender equality, access to diverse goods, and freedom from extreme poverty. These improvements help everyone live healthier, more educated, and more fulfilling lives.
Human Development Index (HDI)
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a tool used to measure and compare the level of development across different countries. It considers three main factors: life expectancy (how long people are expected to live), education (access to schooling and universities), and income (opportunity to earn a high wage). The HDI scale goes from 0 to 1, where 1 represents the highest level of development. Countries like Israel and Qatar have high HDI scores, indicating better living conditions and opportunities for their citizens.
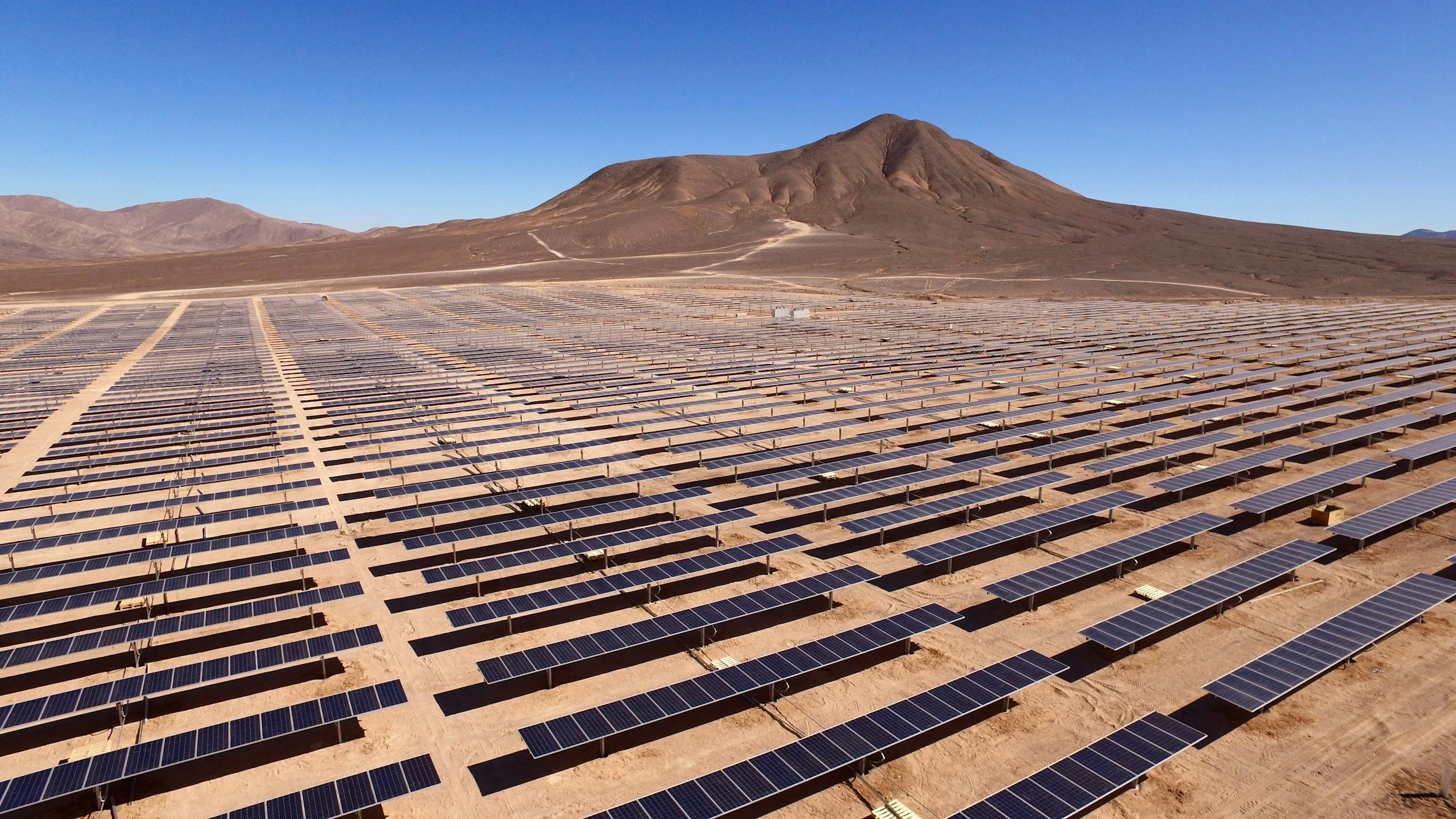
Importance of Oil
Oil is a crucial resource in the world, especially in the Middle East. Countries with abundant oil resources, such as Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the UAE, can use the money earned from selling oil to fund public services and infrastructure. This wealth helps to build schools, hospitals, and roads, which are vital for development. However, relying too much on oil can also pose risks if oil prices fall or if the oil runs out.
Rocky Relationships
The UK and the Middle East have had a difficult history, especially concerning oil. For example, in 1973, during the Yom Kippur War, the UK supported Israel, and in response, many Middle Eastern countries stopped selling oil to the UK. This caused oil prices to rise quickly, which made energy much more expensive in the UK. These historical tensions make trade decisions tricky.
Plentiful and Cheap Reserves
The Middle East has a lot of oil, making up 34% of the world’s production. Because there's so much oil and because the technology for getting the oil has gotten better, it costs less. For the UK, buying oil from the Middle East could mean lower prices and a reliable supply, which is good for keeping energy costs affordable.
Relationship Between Oil and Development
The relationship between oil reserves and a country's development can vary greatly, impacting the quality of life and economic stability of its citizens. The wealth generated from oil can lead to significant improvements in public services and infrastructure if managed wisely. However, it can also lead to challenges if not used sustainably.
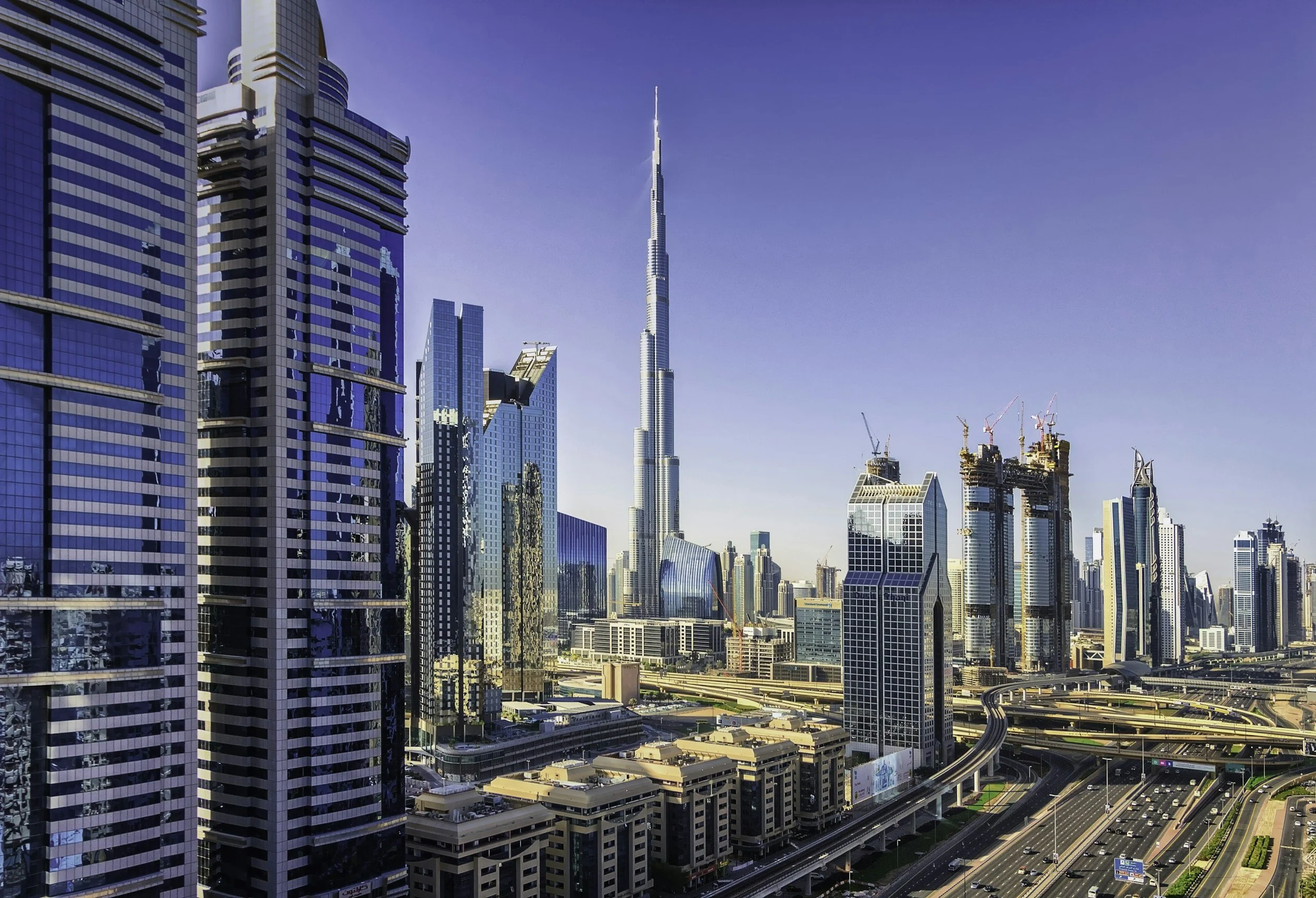
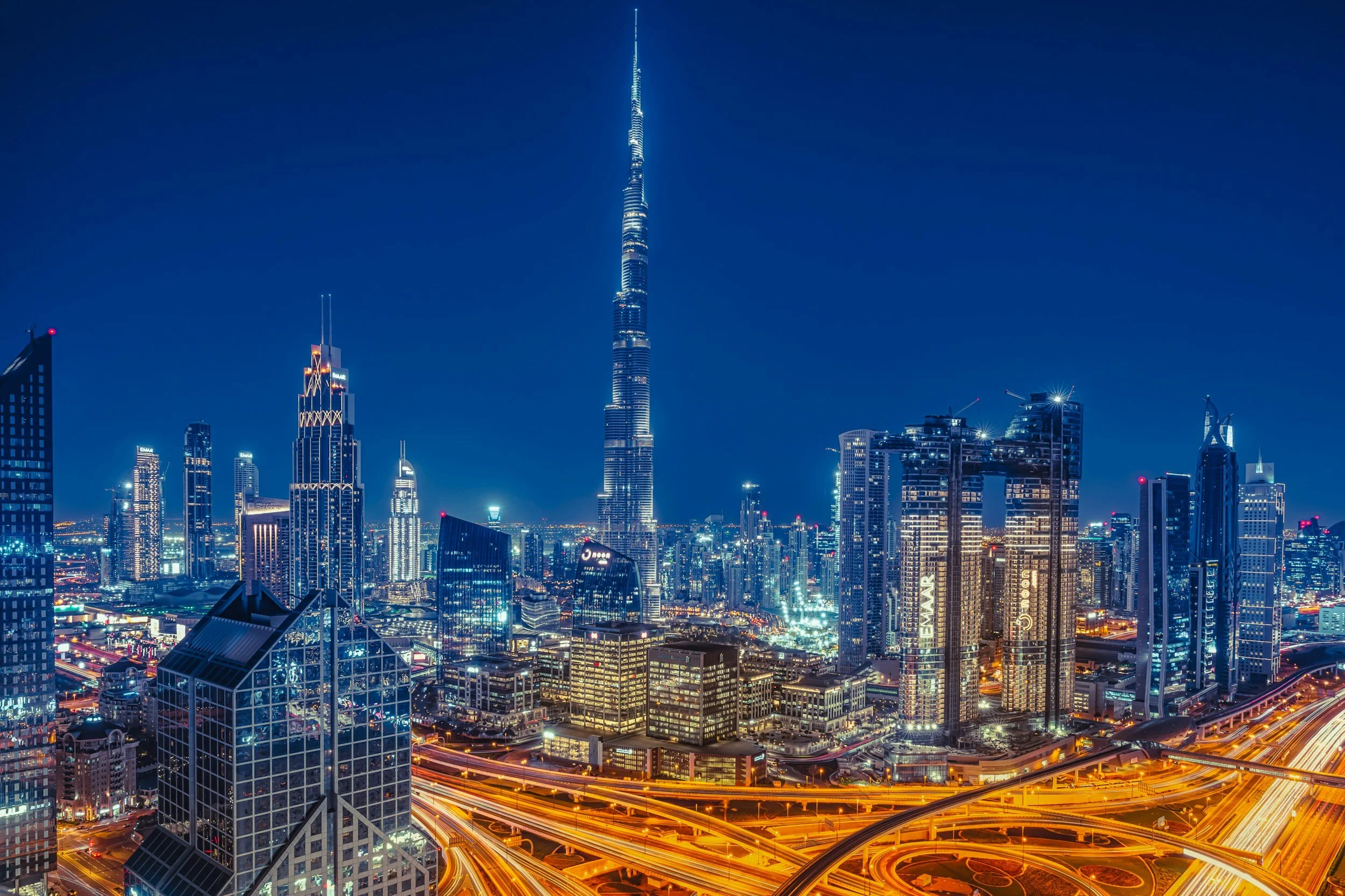
Example of Positive Impact: United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE has successfully used its oil wealth to transform its economy and society. Revenue from oil has funded the construction of world-class infrastructure, including roads, airports, and skyscrapers like the Burj Khalifa in Dubai. The country has also invested heavily in education and healthcare, leading to improved literacy rates and health outcomes. Additionally, the UAE is diversifying its economy beyond oil, investing in sectors like tourism, finance, and technology, which contributes to sustainable development and reduces dependence on oil.
Example of Negative Impact: Nigeria
Contrasting with the UAE, Nigeria, despite being one of the largest oil producers in Africa, has experienced significant challenges due to its oil wealth. The country has struggled with corruption and mismanagement of oil revenues, which has hindered its development. Much of the oil wealth has been concentrated in the hands of a few, leading to widespread poverty and underinvestment in critical public services like education and healthcare. Environmental degradation in oil-producing regions has also caused further economic and health difficulties for local communities.
Should the UK Trade with the Middle East?
The UK needs to decide if it should keep trading for oil with the Middle East. This decision is complex because of the UK's high need for energy, the benefits of Middle Eastern oil, and the challenges of international relationships and alternative energy sources.
Alternative Energy
The UK also has options to use energy sources other than oil, like wind, solar, or hydroelectric power. These alternatives are better for the environment because they don't produce as much pollution. However, they are often more expensive than oil, and setting up the necessary technology takes time and money. The decision to invest in these technologies depends on balancing long-term benefits for the environment with the higher initial costs.
Thirst for Fuel
The UK consumes a lot of energy and has historically relied on fossil fuels like oil, gas, and coal. As its own oil supply has decreased, the need to import oil has grown. This makes the decision to buy oil from the Middle East important because it affects how much people pay for energy and how reliable that energy supply is.
The Ilisu Dam
The Ilisu Dam, located on the Tigris River in Turkey's Southeastern Anatolia region, was completed in 2018 and began filling its reservoir in 2019. It is a massive structure, 138 meters high and 1,820 meters wide, designed to hold up to 10.4 billion cubic meters of water. The dam serves several purposes, including hydroelectric power generation, which provides about 1,200 MW of power, contributing around 2% of Turkey's national electricity needs. It also plays a significant role in flood control and water storage.
Impact and Controversy
The dam has been a subject of significant controversy, primarily due to its environmental impact and the displacement it has caused. The construction led to the flooding of Hasankeyf, a historic town with a history stretching back 10,000 years, and affected 199 settlements in the area. This has raised concerns about cultural heritage preservation and the environmental consequences of such a large-scale project. Additionally, there are geopolitical tensions, as the dam affects water flow into Iraq and Syria, which can exacerbate regional conflicts over water resources.
Turkey's Perspective
Turkey views the Ilisu Dam primarily as a means to generate hydroelectric power and improve water resource management within its Southeastern Anatolia Project. This initiative aims to boost the region's economy through increased energy production and agricultural irrigation capabilities. Turkey asserts that these developments are within its sovereign rights to utilize national resources for economic growth.
In summary…
Impact on Syria
For Syria, the concerns regarding the Ilisu Dam are largely tied to its downstream effects on water availability. The dam's construction has exacerbated existing tensions over water resources, particularly because Syria, being downstream, depends significantly on water flows that originate in Turkey. The reduced water flow from the Tigris threatens agriculture and water supply in regions already stressed by internal conflicts and economic challenges.
Impact on Iraq
Iraq has perhaps been the most vocal against the construction of the Ilisu Dam. The reduction in water flow from the Tigris due to the dam poses severe risks to agriculture, drinking water supplies, and overall ecological health of areas downstream. Iraq views the dam as a threat to its water security, contributing to worsening agricultural conditions and increasing the risk of waterborne diseases due to higher concentrations of pollutants in reduced river flows. Moreover, Iraq has objected to the dam at various international forums, arguing that it has not been adequately consulted and that the project violates international norms on transboundary water resources management.
While Turkey sees the Ilisu Dam as a beneficial project for its domestic energy and agricultural policies, Syria and Iraq are adversely affected by reduced water flows, which impact their agricultural output, water quality, and overall environmental health. These divergent views have led to increased regional tensions over water resources, necessitating calls for more effective transboundary water management and cooperation.
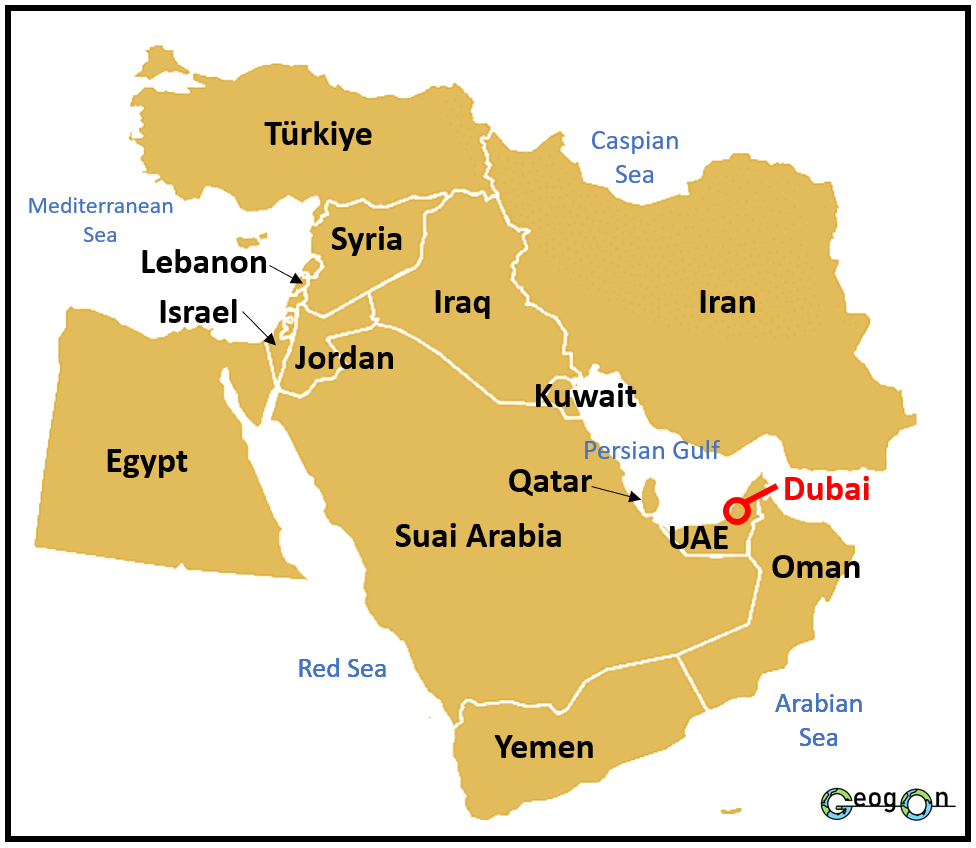
Where is Dubai?
Dubai is a city, it is not a country!
Dubai is strategically located in the United Arab Emirates along the southeast coast of the Persian Gulf. It shares borders with Abu Dhabi to the south, Sharjah to the northeast, and Oman at the southeastern tip. This prime location has helped Dubai become a global hub for trade, tourism, and finance. The city is a gateway between the East and the West, which adds to its economic vitality.
What is Sustainability?
Sustainability involves managing resources so future generations can use them too. It's about finding a balance between economic growth, social inclusivity, and environmental protection. For instance, sustainable practices ensure that fishing doesn’t deplete fish stocks completely, allowing them to replenish over time.
Sustainability is a 3 legged stool. For it to work it must have all 3 legs. The legs of sustainability are:
Social sustainability
Economic sustainability
Environmental sustainability
Is Dubai Sustainable?
Evaluating Dubai's sustainability involves looking at how it manages its social, economic, and environmental challenges and opportunities:
Social Sustainability:
Dubai faces significant challenges in social sustainability, particularly concerning the treatment of migrant workers. Many migrants work under harsh conditions with low pay, long hours, and inadequate living conditions. Despite these challenges, Dubai also exhibits strengths in social sustainability. It is one of the most multicultural cities globally, hosting residents from over 200 countries, which enhances cultural diversity and integration. Additionally, the city is known for its low crime rates and high standards of healthcare, contributing positively to the quality of life for its residents.
Environmental Sustainability:
Environmentally, Dubai faces severe challenges due to its extreme climate and limited natural water resources. The city has one of the highest water consumption rates globally, heavily reliant on energy-intensive desalination processes. Additionally, the majority of its energy is derived from burning natural gas, a fossil fuel, which has significant environmental impacts. On a positive note, Dubai has invested in renewable energy sources, including a substantial solar power plant that significantly reduces CO2 emissions and plans for expansion are in place to increase its capacity.
Economic Sustainability:
Economically, Dubai has made significant strides towards sustainability. The city has diversified its economy well beyond its historical reliance on oil revenues. Now, the service industry, including retail and tourism, plays a significant role in its economy. Dubai's global trade is facilitated by its strategic location and extensive shipping routes, connecting it with markets around the world. This diversification helps stabilize its economic future and reduces vulnerability to oil price fluctuations.
In summary, while Dubai has made commendable progress in certain areas of sustainability, significant challenges remain, particularly in environmental management and social equity. These issues require ongoing attention and strategic planning to ensure a balanced sustainable development.
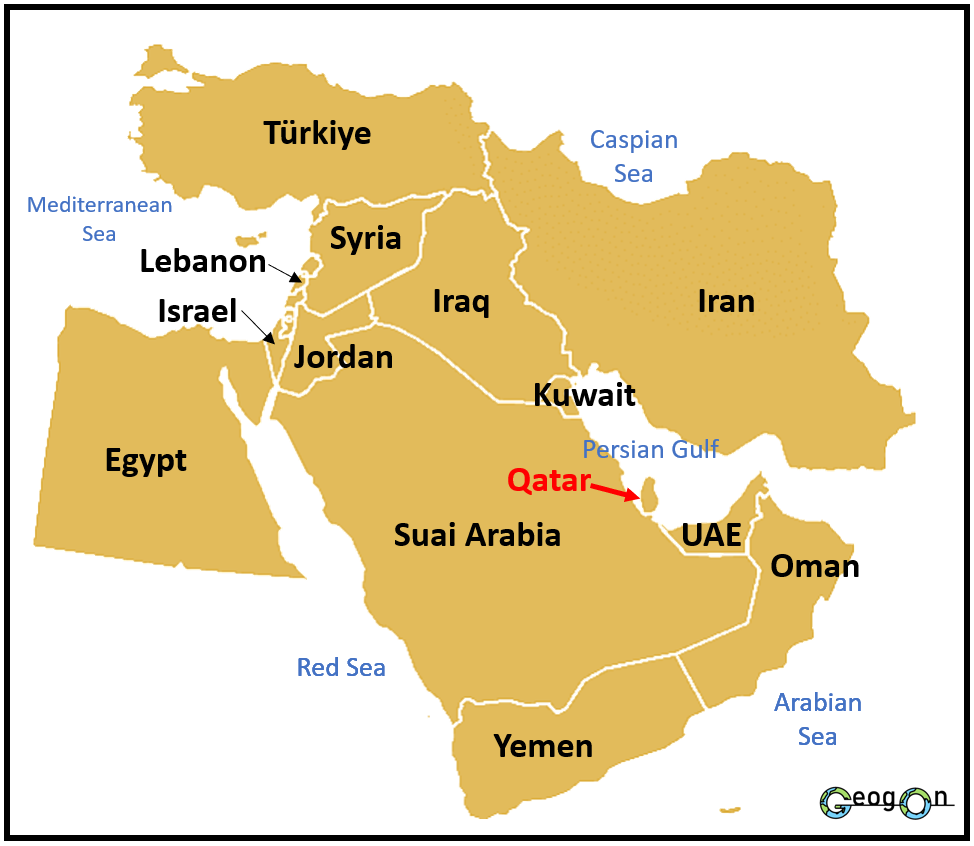
Where is Qatar?
Qatar is located in the Middle East, on the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by the Persian Gulf on the north and east, the Gulf of Bahrain on the northwest, and shares a land border with Saudi Arabia to the southwest. The country is also close to the UAE and Bahrain.
Qatar's Climate
Qatar has a desert climate with extremely hot summers, where temperatures can reach up to 41.5°C. The highest rainfall occurs in February but generally, the region receives very little rain.
What is the football World Cup?
The World Cup is a soccer/football competition where teams from different countries compete to see who is the best in the world. It happens every four years and is organized by FIFA, which is the international governing body for soccer/football.
Why Is It Important?
The World Cup is important because it brings people from all over the world together to enjoy soccer. It celebrates different cultures and shows the value of teamwork and fair play. Winning the World Cup is considered the highest achievement in international soccer.
Economic Benefits
Hosting the World Cup can boost the economy of the host country. It brings in thousands of tourists who spend money on hotels, restaurants, and other attractions. The event also creates jobs, both temporarily and sometimes permanently, in sectors like construction, hospitality, and security.
Why would a country want to host the World Cup?
Human Rights Concerns
Qatar has faced significant criticism for human rights abuses, particularly concerning the treatment of migrant workers involved in constructing World Cup infrastructure. Reports have highlighted issues such as appalling treatment, modern slavery conditions, and a high number of deaths and injuries among workers. These conditions raise ethical questions about the appropriateness of Qatar hosting such a significant global event.
Improved Infrastructure
To prepare for the World Cup, countries often improve their infrastructure. This can include building new sports stadiums, upgrading airports, and enhancing transportation systems. These improvements not only serve for the event but also benefit the local population long after the tournament has ended.
Cultural Exchange
Hosting the World Cup allows for significant cultural exchange. People from different countries bring their unique cultures, creating a festive, inclusive atmosphere. This helps promote understanding and goodwill among nations.
Global Recognition
Hosting the World Cup puts a country on the global stage, attracting international attention. This can enhance the host country’s image and prestige, potentially leading to increased tourism and foreign investment long after the event.
National Pride
Hosting a successful World Cup can boost national pride. It allows the host country to showcase its culture, history, and achievements to a global audience.
Should Qatar Have Hosted the 2022 World Cup?
Deciding whether Qatar should have hosted the 2022 World Cup involves considering various factors, including human rights, economic impacts, the climate and infrastructural changes.
Economic and Infrastructural Developments
Qatar embarked on an ambitious $200 billion modernization program to prepare for the World Cup, which included constructing state-of-the-art stadiums and improving the country's infrastructure. While these developments have boosted the country's global image and economy, the means by which they were achieved — particularly the exploitation of migrant labor — have been widely criticized. Also the projects consume a considerable amount of space, which is limited in Qatar.
The Climate
The climate of Qatar poses another significant challenge for hosting the World Cup. Known for its extremely hot and arid conditions, Qatar experiences temperatures that can soar above 40°C (104°F) during the summer, which is when the World Cup traditionally takes place. Such extreme heat raises serious concerns about the health and safety of players, officials, and fans. The methods used to counteract the heat, such as extensive air conditioning, have a significant environmental impact, contributing to high energy consumption and carbon emissions. This raises questions about the sustainability of such measures in the face of global efforts to combat climate change.
Conclusion
The decision on whether Qatar should have hosted the World Cup is complex. On one hand, the event has brought significant economic benefits and global attention to Qatar. On the other hand, it has highlighted severe human rights issues that cast a shadow over these achievements. The controversies surrounding Qatar's preparations for the World Cup underscore the need for major sporting events to consider ethical implications as much as economic or logistical ones. The ongoing criticism suggests that while infrastructure can be built, true sustainability and ethical governance are still areas where Qatar — and similar host countries — need to make substantial improvements.